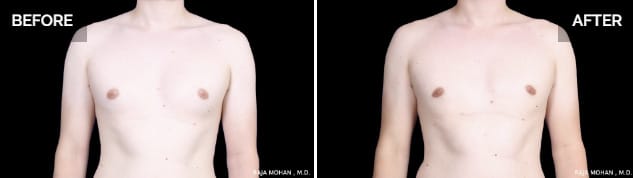
Gynecomastia sets itself apart from regular chest fat primarily because it is predominantly unresponsive to lifestyle modifications, specifically diet and exercise. Rather, it stems from an abnormal growth of glandular tissue and is often associated with hormonal imbalances.
Men frequently express concern over the presence of noticeable breast tissue and seek ways to eliminate it. The desire for a well-defined, flat chest with muscular pectorals is a common aspiration among many.
Before a plastic surgeon can address the issue of excess breast tissue with Gynecomastia Surgery in Dallas, however, it’s important to figure out what’s causing it. Below, we’ll take a closer look at gyno vs chest fat and how to tell the difference.
First, let’s define gynecomastia.
WHAT IS GYNECOMASTIA?
Gynecomastia can be described as swollen male chest fat. Reduced male hormones tend to be the most common cause of this condition (more on this later). However, there are other reasons it may occur as well.
Depending on the root cause, the most common symptoms of male gynecomastia are:
- Enlargement of the breast tissue
- Excess chest fat
- Swelling
- Feeling lumps in the breast/chest
- Tenderness
- Chest discomfort
- Weight gain or obesity
 WHAT CAUSES GYNO VS CHEST FAT?
WHAT CAUSES GYNO VS CHEST FAT?
Gynecomastia is actually quite common in males of nearly all ages. However, some types of gynecomastia will go away on their own while other types will stick around, and often, only cosmetic surgery can fix the latter.
The causes for having gynecomastia range from having a hormonal imbalance or a related illness to using illicit substances or taking certain medications. Below, we’ve outlined the main causes of gynecomastia in males.
HORMONAL IMBALANCE
A hormonal imbalance is the most common cause of gynecomastia. Hormonal imbalances in males can take place at any age.
Even newborn baby boys can experience this issue because they often receive excess estrogen (a female hormone) from their mothers. When gynecomastia is present in newborn baby boys, it is often referred to as having “breast buds”. These breast buds generally go away within a few months after birth, but they may sometimes last longer.
Preteen boys often experience “breast buds” as well, prior to puberty. And in young men going through the actual stages of puberty, gynecomastia is also relatively common. Again, the issue generally disappears within half a year or sometimes up to two years.
On the other hand, for at least some reduction of men, adulthood may be reached and gynecomastia is still an issue. Again, this can usually be traced back to a hormonal imbalance. Sometimes, a cancer of the hormonal glands (adrenal, pituitary, etc.) can be the cause of this imbalance — or testicular or liver cancer. Regardless of the root cause, males with gynecomastia generally produce too much estrogen and not enough testosterone.
MEDICATIONS
Certain medication can cause gynecomastia as well. Generally speaking, these are medications that have high levels of substances such as prolactin or that increase the levels of estrogen in the body.
There are also medications that may block androgens. Testosterone and DHT are types of androgens. Not only do these work on their own, but they also block the effects of estrogen. Therefore, if an individual is taking a medication that blocks androgens like testosterone or DHT, the effects of estrogen will become more pronounced, and this can cause gynecomastia.
Some examples of medications that may have gynecomastia as a side effect include:
- Some antianxiety medications
- Some antidepressant medications
- Some epilepsy medications
- Certain drugs used for the treatment of heart conditions such as digitalis
- Anti-androgen drugs
- Certain medications that are used to treat ulcers
- Certain drugs used in chemotherapy, specifically alkylating agents, which inhibit the growth of cancer cells and can also interfere with cell DNA
Although not technically medications, some herbal supplements and essential oils have also been linked to gynecomastia by certain sources — specifically, tea tree oil and lavender oil.
MEDICAL CONDITIONS AND ILLNESSES
As stated above, certain medical conditions and illnesses that are related to hormones can lead to gynecomastia. This includes cancer of the adrenal glands, cancer of the pituitary, glandular breast tissue, and testicular cancer. An overactive thyroid can also be the cause, as can lung cancer.
Other medical conditions and illnesses can also cause excess breast tissue. For example, illnesses that are related to the liver specifically the breast glands, such as cirrhosis of the liver (often caused by alcoholism) or liver cancer, can be the root problem.
SUBSTANCE USE
In addition to certain medications, taking certain drugs and illicit substances can cause gynecomastia.
For example, the excessive consumption of alcohol may be related to the condition. Other drugs that have also been linked include marijuana, amphetamines, opioids, anabolic steroids, and methadone (most commonly used to treat addiction).
PUBERTY AND “PRE-PUBERTY”
Finally, young men who are going through puberty or “pre-puberty” (technically referred to as precocious puberty) may have excess breast tissue.
Pre-puberty is any time below the age of 9 when a young boy’s body is changing and growing rapidly. Male puberty occurs from about the age of 9 to the ages of 15 or 16 and is also characterized by rapid physical changes as well as extreme hormonal fluctuations.
Therefore, if a male is anywhere from childhood to age 15 or 16, if they have “breast buds” or excess breast tissue, this is nearly always perfectly normal and should be left alone.
GYNECOMASTIA VS Chest FAT: WHAT’S THE DIFFERENCE?
Is it gynecomastia or chest fat?
We receive this question a lot, and it makes sense. Male patients come into our office wanting to get rid of the excess tissue on their chests. They may feel self-conscious about it, especially when not wearing a shirt at the beach or pool or when wearing thinner materials that make body contours more noticeable.
Here are 7 questions to ask if you are concerned about excess tissue on your own chest area, and want to know if it’s caused by.
IS IT GYNECOMASTIA VS FAT? 7 QUESTIONS TO ASK
1. WHAT’S YOUR AGE?
If you are a young man who has yet to go through puberty and you have excess fat and/or tissue on your chest, this could simply be related to your age. Gynecomastia surgery should never be performed on young men who are going through puberty or “pre-puberty” as time is almost always the best cure.
Your hormones will work themselves out. And especially if you maintain a healthy and nutritious diet and regular exercise, it is almost certain that your chest will flatten and you’ll feel more comfortable by around age 15 or 16.
Conversely, older males may experience excess breast tissue later in life due to hormonal changes — especially the natural drop in testosterone. This is particularly true for men who are older and overweight or obese.
2. DO YOU HAVE ANY EXCESS BODY FAT?
Most doctors can simply take a look at your overall body composition to know if it’s gynecomastia vs just fat. Overweight and obese men will naturally have a distribution of excess fat on their bodies, some of which may settle in the chest.
There are also body composition tests that can be performed to determine your body’s actual fat percentage. Even seemingly trim men who appear to have a low percentage of body fat may actually be what is sometimes referred to as “skinny fat”. This means that the body has a low proportion of muscle and an elevated body fat percentage.
Another marker can be cholesterol and triglyceride levels. After blood tests, if you find that you have high triglycerides, low HDL cholesterol (“good” cholesterol), and/or high LDL cholesterol (“bad” cholesterol), this could be linked to a higher percentage of body fat, which may settle in the chest.
3. DO YOU HAVE A MEDICAL CONDITION?
As stated above, gynecomastia treatment can also be traced back to certain medical conditions — many of which are related to hormones. For example, hormonal imbalance is common in men who have an overactive thyroid or who have cancer of the testicles, pituitary gland, or adrenal glands.
Liver and lung cancers have also been linked to excess breast tissue. Kidney disease and kidney failure and cirrhosis and liver failure may also be linked to the problem.
4. HAVE YOU HAD YOUR HORMONES CHECKED RECENTLY?
It’s not uncommon for hormonal imbalances to go unnoticed in both men and women. If you or your doctors suspect that excess estrogen, a lack of testosterone, or another hormone-related issue may be causing your gynecomastia, be sure to have your hormones checked.
A simple lab test is usually all that is needed. Testosterone levels are generally highest in the morning, so this is usually when your doctor will have you have your blood drawn at a local lab. Test results should be available within the day in most cases or within a week at maximum.
5. WHAT’S YOUR DIET LIKE?
If you have a high percentage of body fat — even if you are within a relatively healthy weight range — this can cause excess skin tissue to form in the breasts.
It’s important for men of all ages to consume a healthy diet of protein, whole grains, vegetables, fruits, and healthy fats and oils. Enjoying treats in moderation won’t ruin an overall healthy diet, however, it’s also wise to avoid excess processed foods.
6. HOW OFTEN DO YOU EXERCISE?
Strength training, specifically, can help to define the pectoral muscles and make excess tissue and fat less apparent. If the amount of excess tissue you have is minimal, try chest-strengthening exercises to increase definition.
7. DO YOU DRINK ALCOHOL FREQUENTLY OR USE SUBSTANCES?
We’ve already gone over the fact that excess alcohol use and the use and abuse of substances such as opioids, marijuana, and amphetamines can be linked to gynecomastia.
If you are abusing illicit substances, get the help you need by reaching out to a trusted friend or family member. You can also seek help from your family doctor or another medical professional.
MALE BREAST REDUCTION SURGERY: A SOLUTION FOR DALLAS GYNECOMASTIA
The American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS) estimates that as many as 70% of men will have gynecomastia treatment have enlarged tissue of the breast at some point. Although the condition is often temporary and will improve with age or lifestyle changes, for many men with actual gynecomastia, the only solution is male breast reduction surgery.
WHAT HAPPENS DURING MALE BREAST REDUCTION SURGERY?
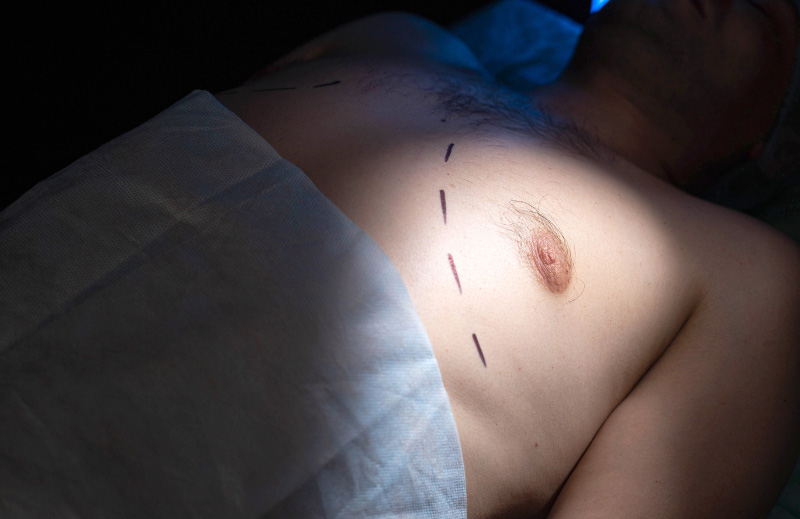
Male breast reduction surgery (or gynecomastia surgery) helps to fix the problem of excess chest fat in males.
The procedure involves the removal of both the excess glandular tissue and any excess fat — usually by way of Dallas liposuction. In some cases, an excision technique may be used alone or in addition to liposuction.
For patients who would like to make their nipples and areolas smaller, this can be done during the same surgery in most cases. Exactly how your gynecomastia surgery will be performed is something your surgeon can discuss with you at your consultation appointment.
FAQ: GYNECOMASTIA VS CHEST FAT
DOES LOSING FAT GET RID OF GYNECOMASTIA?
If a patient has true gynecomastia that is related to a hormonal imbalance, medical condition, substance use, medication use, etc., then no, overall fat loss alone will not likely fix the problem of gynecomastia.
For patients with gynecomastia, usually only surgical treatment or male breast reduction surgery will improve the problem.
IS GYNECOMASTIA ALWAYS IN BOTH BREASTS?
No, it is possible for men to have gynecomastia in only one breast. It is, however, more common to experience this condition in one or both breasts.
HOW COMMON IS GYNECOMASTIA?
Gynecomastia is extremely common, with up to 70% of all men experiencing it at some point in their lives. Most of the time, however, the excess tissue in the breasts is temporary.
In severe cases in younger males, time will generally rectify the issue. In men in their 20s and beyond, strength training, cardiovascular exercise, and fat loss through consuming a healthy diet can help. When these solutions don’t help, male breast reduction is an option.
How do you tell if you have gynecomastia or just fat?
In contrast to gynecomastia, chest fat may lack a well-defined shape, often exhibiting a saggy or droopy appearance. If chest fat is the culprit, shedding excess weight should result in a noticeable reduction in the size of the pectoral region. Similar to fat in other parts of the body, chest fat responds to diet and exercise as part of overall body fat.
SCHEDULE YOUR GYNECOMASTIA CONSULTATION
Do you have enlarged breast tissue or excess chest fat that you would like to get rid of?
Dr. Raj can help you determine if the cause of your excess chest tissue is gynecomastia and fat or just gyno. Dr. Raj can help answer any questions you may have about gynecomastia before and after expectations. For many patients, male breast reduction surgery can help you get your sleek physique back with minimal scarring.
Call today to schedule your consultation.
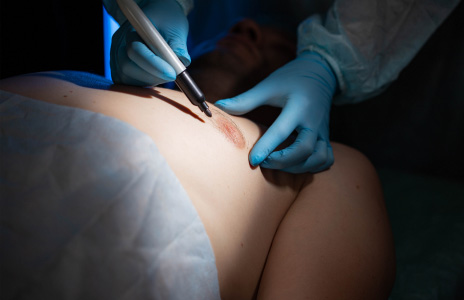 WHAT CAUSES GYNO VS CHEST FAT?
WHAT CAUSES GYNO VS CHEST FAT?